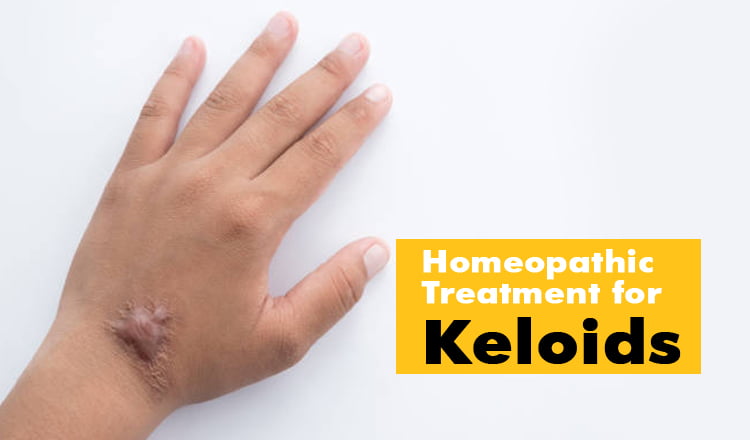
Keloids are overgrowths of scar tissues or granulation tissue on the skin. It occurs at the skin site where a person had an injury. It is a skin disorder. Though the injury is healed, scars composed of collagen type 1 is formed on the skin. These raised, firm, rubbery and shiny lesions are called keloids or keloidal scars. Keloids vary in colour and size. The shades range from pink, red to dark brown. Mostly, keloidal scars are benign. A person may experience skin irritation, pain and itchiness.
Keloids are often observed on the face, earlobes, breast bone or upper chest and the back. Over time a keloid might undergo some changes in terms of its texture. Young people between the ages of 10 and 30 years of age tend to have keloids especially if members of the family do.
In the United States of America, keloids are observed 15 times more in people of African sub-Saharan descent than in people of European descent. People with grave injuries are at a higher risk of developing keloids.
Recommended reading: Holistic Solution For Fibroids
Signs and Symptoms
Keloids grow out of the limits of the original scar. It encroaches upon normal skin, unlike hypertrophic scars. The sensation on the skin varies from person to person. Keloids are self-diagnosable but are often confused with hypertrophic scars. The common signs and symptoms of keloids are:
- Lumpy skin that looks shiny.
- The texture varies from soft to firm.
- They are hairless and rubbery.
- The sizes vary depending on the size of the scar
- They are thick and irregular.
- Skin irritation and reddening of the affected skin area is a sign.
- Keloids can arise by themselves without any former injury.
What Causes Keloids?
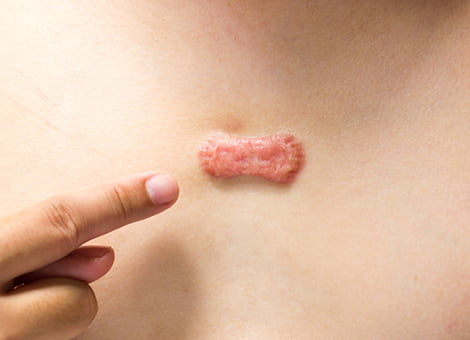
Both genetic and environmental factors can cause keloids. Something from a simple pimple to skin piercing, scratches, tattoos, chickenpox scarring, burns, hair removal, acne or repeated injury and trauma can cause keloids. Still, experts cannot completely identify the cause of keloids. Most of them believe it to be a dysfunction of the healing process. The protein called collagen helps the body to heal. Excess collagen can cause keloids. Complications may arise when keloids at joints tighten or become hard interfering with movement.
Prevention and Treatment of Keloids
Those aware of their family members having keloids should be careful as they are predisposed to develop keloids themselves. They should avoid getting tattoos, body piercings and other cosmetic surgeries as they are at a higher risk of developing keloids. Skin problems of any kind like acne, eczema etc, need immediate attention as people with genetic disposition may develop keloids.
Treatments for keloids are:
- Preventive
- Therapeutic
Preventive treatment includes allopathy and homoeopathic remedies, medicines, corticosteroids, silicone gel sheeting, a healthy diet, boosting the immune system, taking supplements and having nutritious food.
Therapeutic ones include pressure therapy, intralesional triamcinolone acetonide(TAC), radiation, laser therapy (PDL), radiotherapy and cryotherapy.
Surgical removal of keloids is currently the popular treatment method. Treatment of keloids commonly depends on a person’s age. Children cannot be prescribed anti-metabolites and corticosteroids. Even, radiotherapy is not advisable for children. Hence, alternative treatment methods are being developed and administered.
Homoeopathy is the oldest form of natural treatment for skin disorders like keloids. Its popularity and usage are increasing as millions have benefitted from homoeopathy treatment. For children, homoeopathic medicines and products are safer as they hardly have any side effects. Homoeopathy medicines do not cause any growth abnormalities in children unlike other forms of treatment. Therefore, its preference is increasing as an alternative form of treatment. It is now being integrated into the medical system of many countries.
Unlike homoeopathy, surgical treatment does not guarantee a complete cure of keloids. When applied as the sole form of treatment, the recurrence rate of keloids in patients is much greater, ranging from 70% to 100%. Skin lesions of larger size are likely to form on recurrence. Surgical excision combined with other forms of the treatment proves effective. Homoeopathy is considered to be the best alternative for healing surgical scars, preventing the development of keloids. Pressure therapy following surgical procedures and homoeopathy medicine have shown promising results in treating keloids of the ear.
Recommended reading: Best alternative treatment for tonsillitis
Best Homoeopathy Medicines for Keloids
Here’s a list of the best homoeopathic medicines for keloids. Adults and children can both benefit from them.
- Graphites
- Silicea
- Thiosinaminum
- Causticum
- Fluoricum Acidum
- Nitric Acid
- Calendula
- Thuja
- Radium Bromatum
- Phytolacca Decandra



